
Browse by category
- Adaptive reuse
- Archaeology
- Arts and creativity
- Black heritage
- Buildings and architecture
- Communication
- Community
- Cultural landscapes
- Cultural objects
- Design
- Economics of heritage
- Environment
- Expanding the narrative
- Food
- Francophone heritage
- Indigenous heritage
- Intangible heritage
- Medical heritage
- Military heritage
- MyOntario
- Natural heritage
- Sport heritage
- Tools for conservation
- Women's heritage
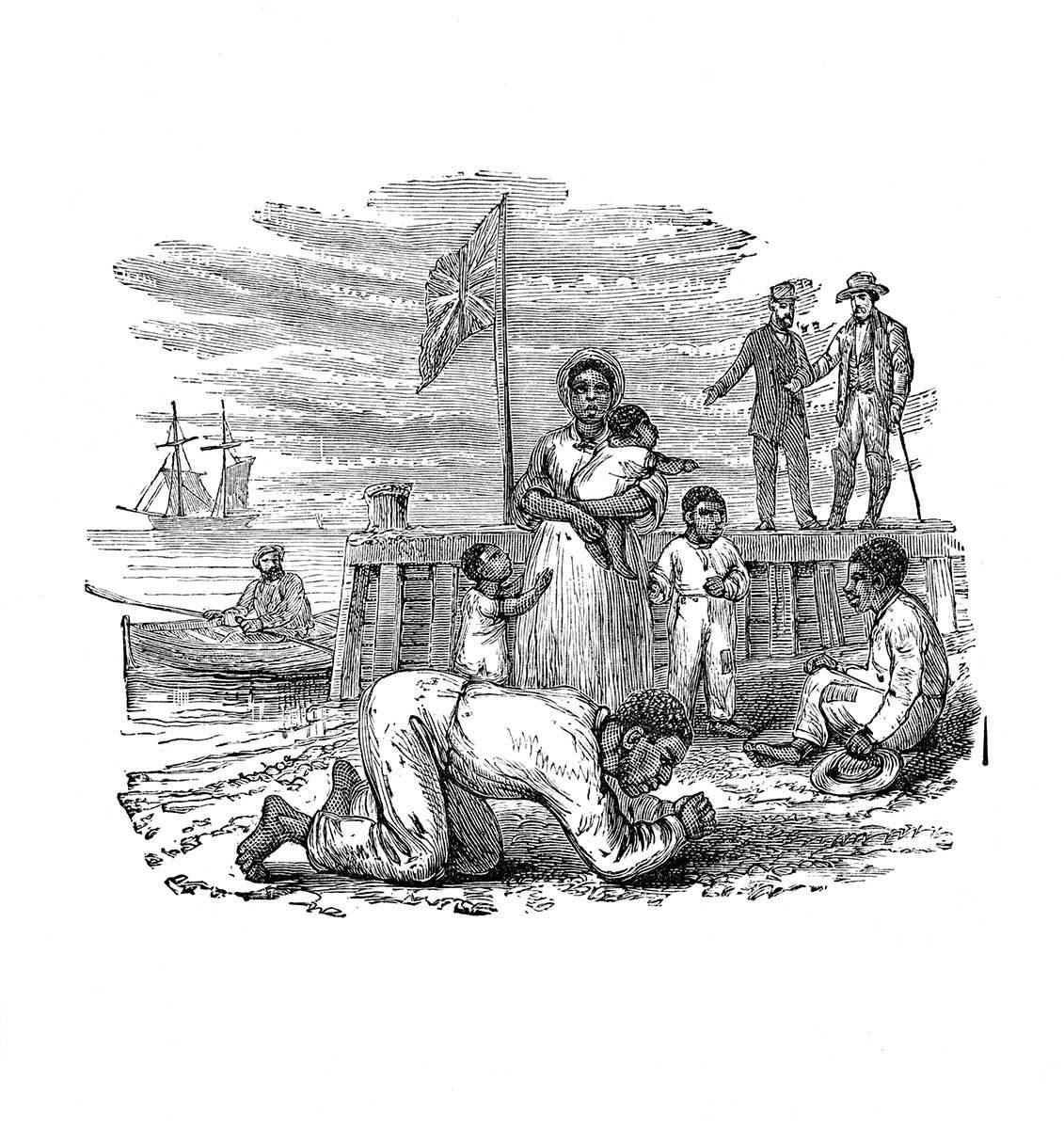
Timeline to freedom
3500 BC to 332 BC – Slavery is practised in ancient Egypt as prisoners are sold as slaves
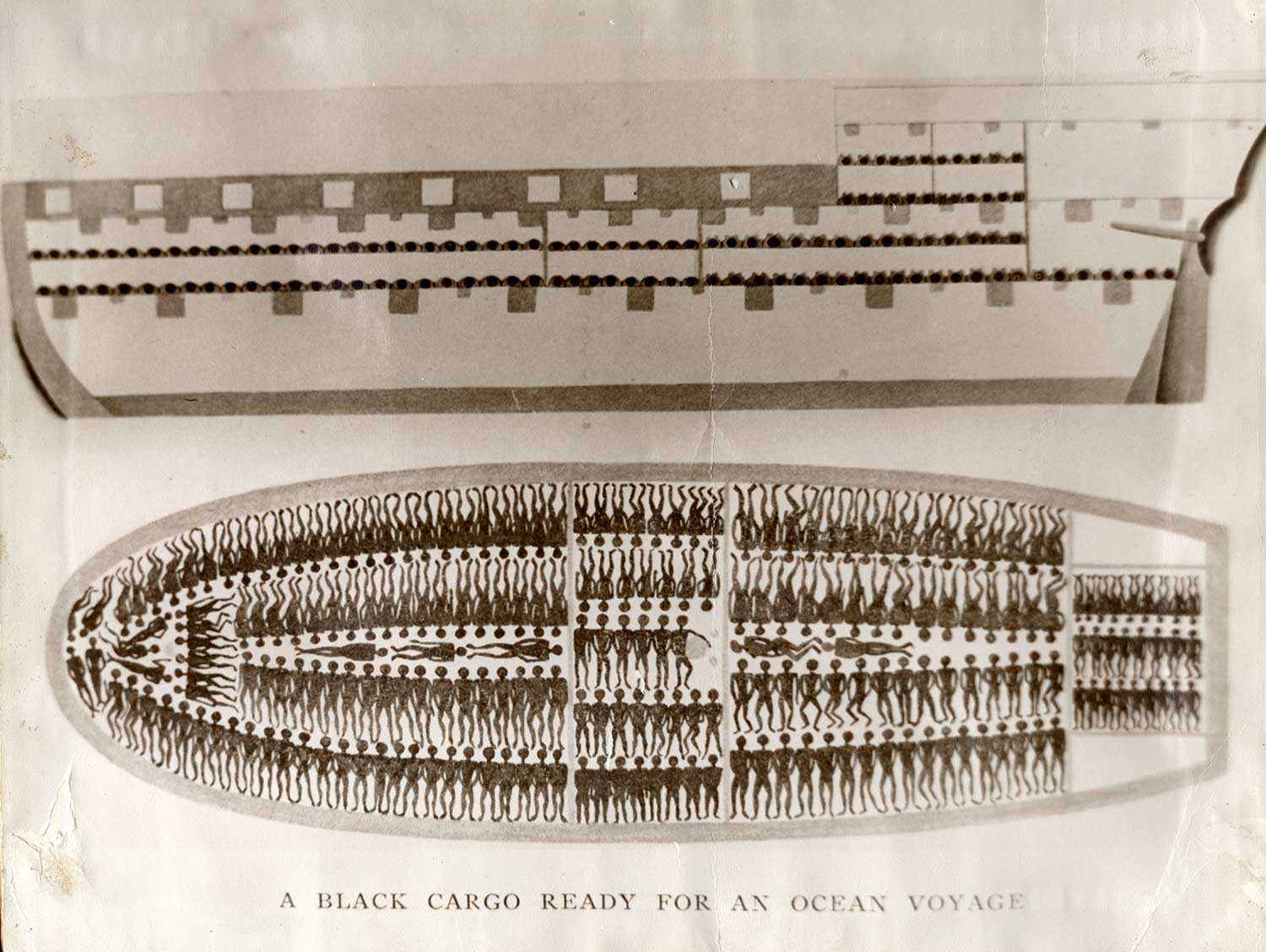
1500s – Beginning of the European slave trade
1605 – Mathieu Da Costa, an African translator hired by Samuel de Champlain, becomes the first Black person to arrive in Canada
1619 – Slavery begins in North America with the arrival in Jamestown, Virginia of a Dutch slave trading ship carrying 20 Africans
1628 – Olivier LeJeune becomes the first recorded slave to arrive in Canada; he was six years old
1793 – Chloe Cooley, an enslaved person, is forced to cross the Niagara River; Black veteran Peter Martin compels Lieutenant-Governor John Graves Simcoe to end slavery
1793 – Simcoe's Act to Limit Slavery becomes the first anti-slavery act in the British Empire; it prohibits the further importation of slaves into Canada and leads to the gradual demise of slavery in Upper Canada
1807 – Britain abolishes the trans-Atlantic slave trade
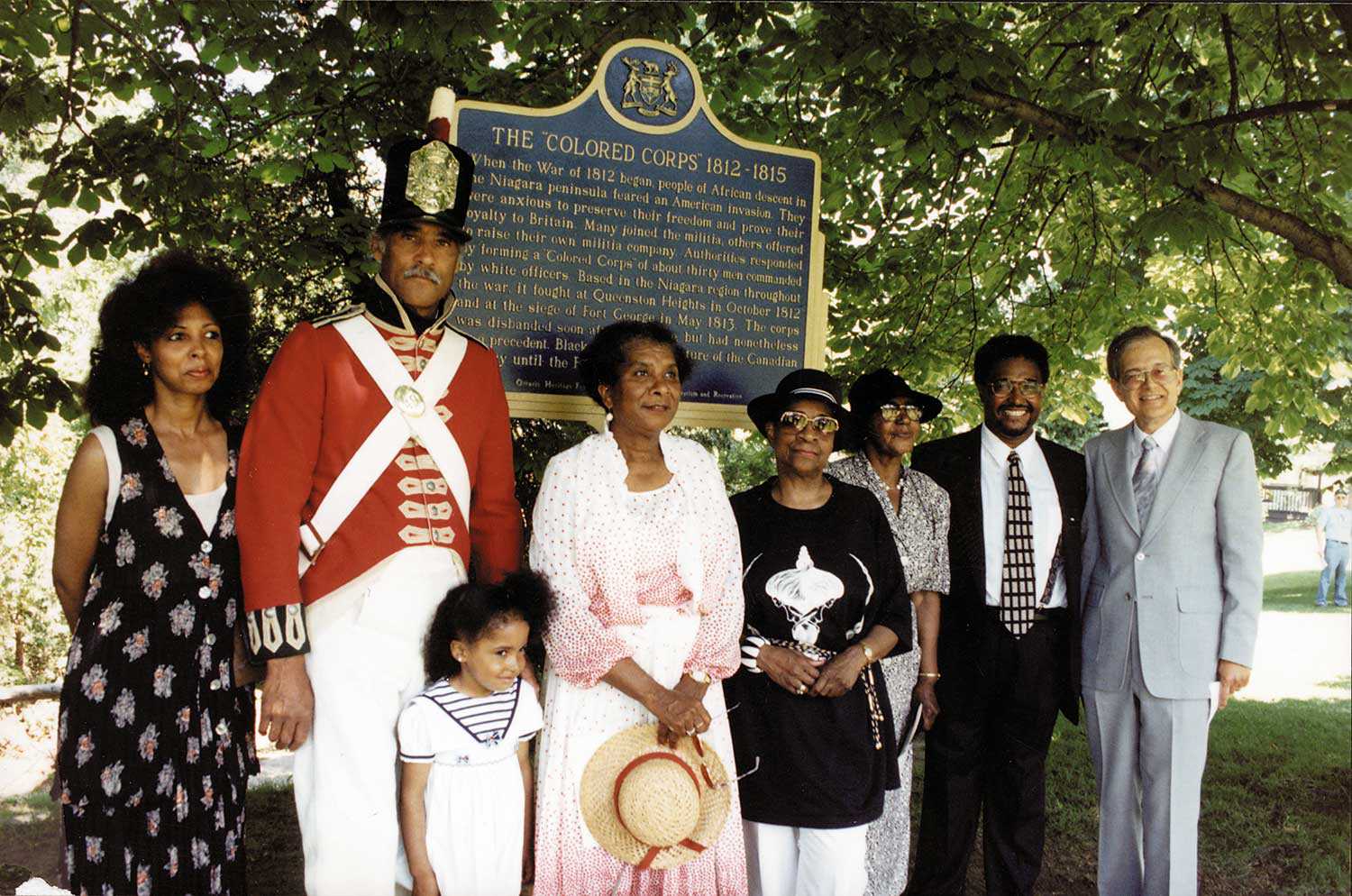
1812 – Black volunteers fight under the British flag in the War of 1812 to defend their home in Canada and prevent a return to slavery
1815 – Black veterans of the War of 1812 receive grants of land in Oro Township, creating an early Black settlement
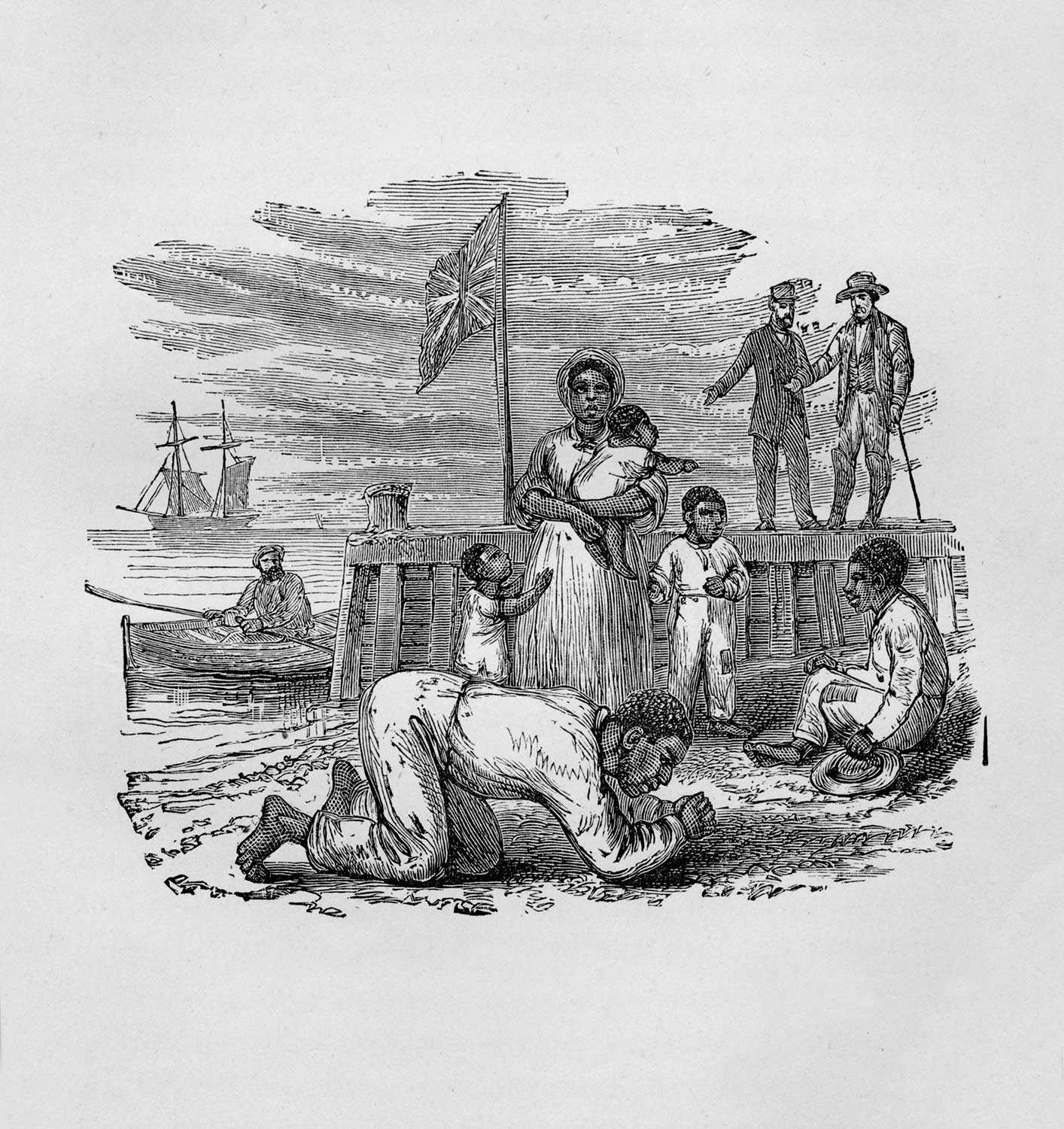
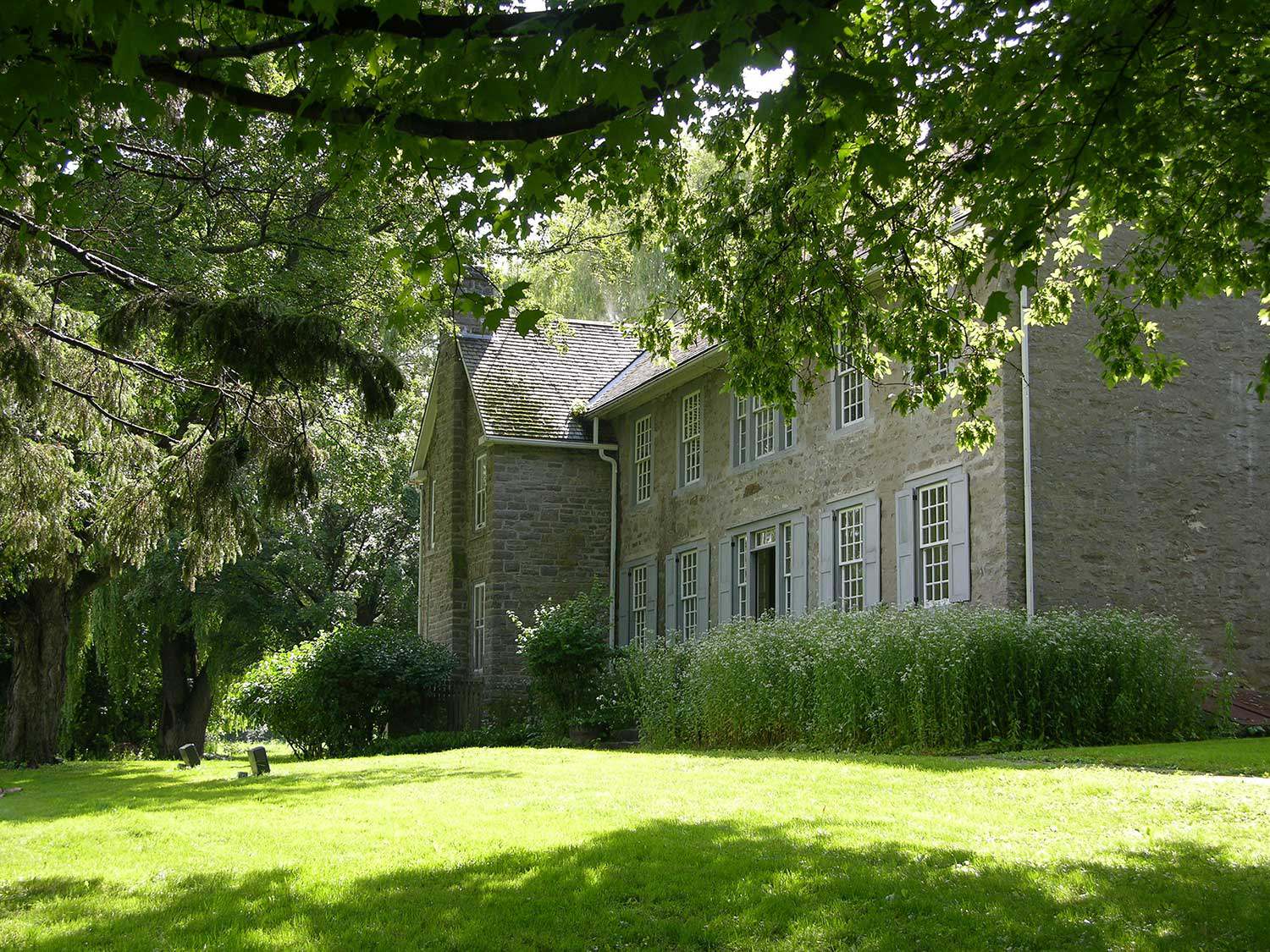
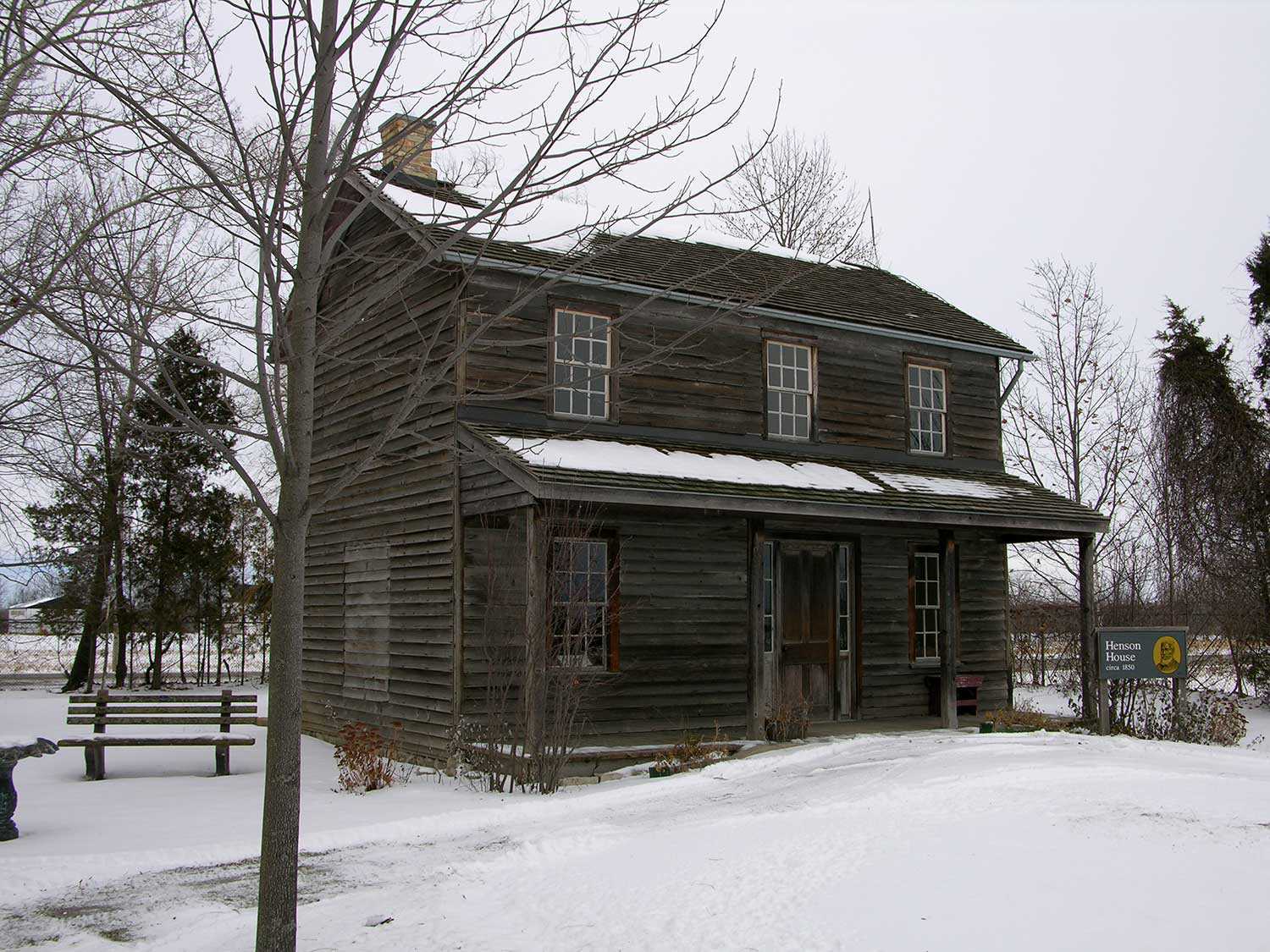
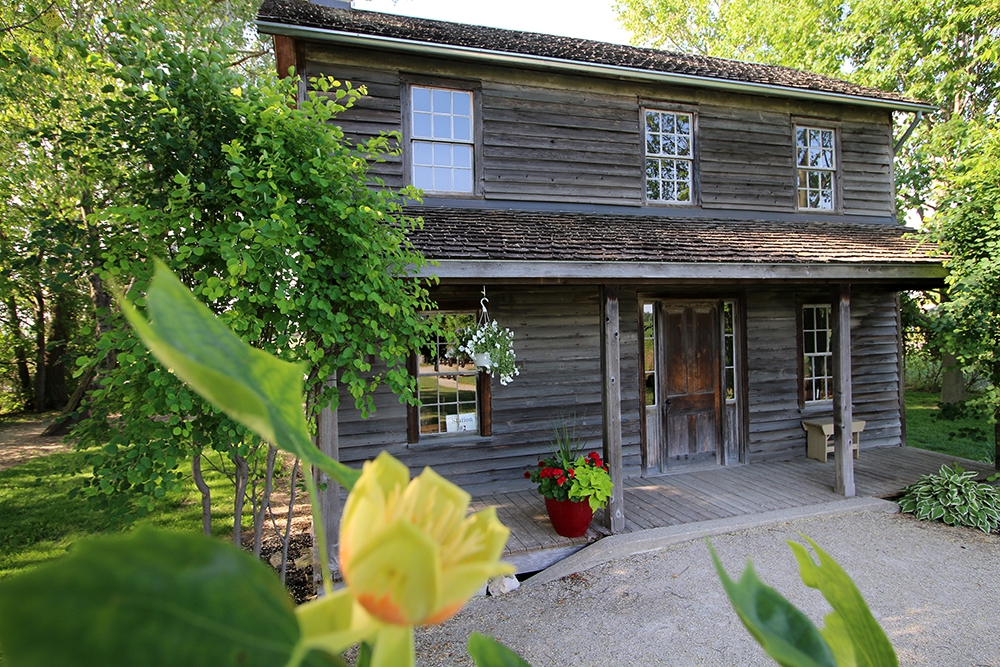
1830 – Josiah Henson escapes to freedom with his wife Charlotte and four children, arriving near Fort Erie, Ontario; Henson goes on to become a leading Black abolitionist and important community leader
1830 – The Wilberforce Settlement, a sizable Black community, is founded by former residents of Cincinnati; the settlement disbands six years later because of poor financial management
1834 – On August 1, slavery is formally abolished across the British Empire; celebrated annually as Emancipation Day
1833 – Solomon Moseby, an enslaved person, comes to Canada from Kentucky only to be accused and arrested for stealing a horse from his former owner; during his transportation back to Kentucky, one of the first race riots in Canada breaks out and Moseby escapes
1837 – Canadian Blacks gain the right to vote
1837 – Black volunteers serve in the "Colored Corps" during the Rebellion of Upper Canada to defend the government and support Black rights
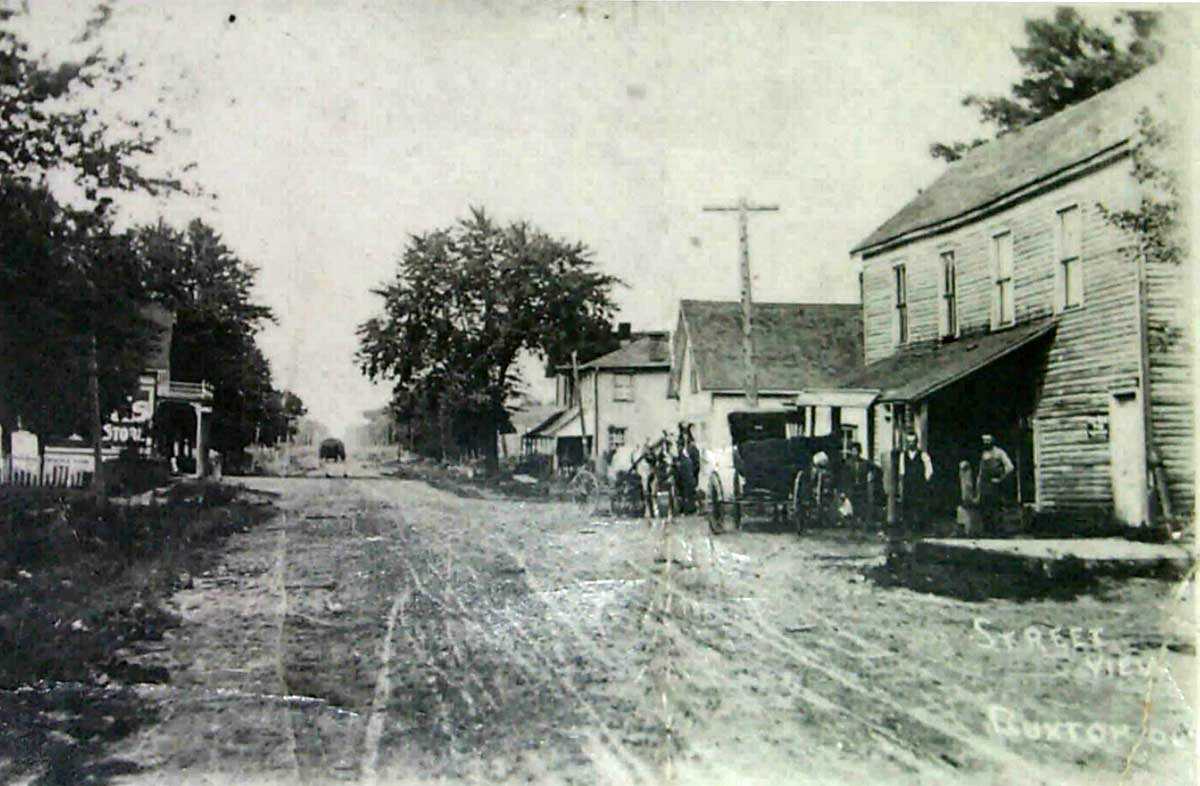
1849 – Fifteen escaped slaves arrive in what is now the Buxton area where Reverend William King purchased land to form a settlement
1849 – Harriet Tubman escapes from slavery and repeatedly returns to the South, travelling the Underground Railroad in reverse to assist enslaved people in their escape to freedom
1849 – The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave – Henson’s autobiography is published
1851 – On January 1, Henry Bibb publishes the first issue of the abolitionist newspaper – the Voice of the Fugitive – in Windsor, Ontario; the Voice reported on the movements of the Underground Railroad
1851 – On February 26, the Anti-Slavery Society of Canada is founded to “aid in the extinction of slavery all over the world;” this society helped those seeking freedom in Canada and worked to influence public opinion on the topic of slavery
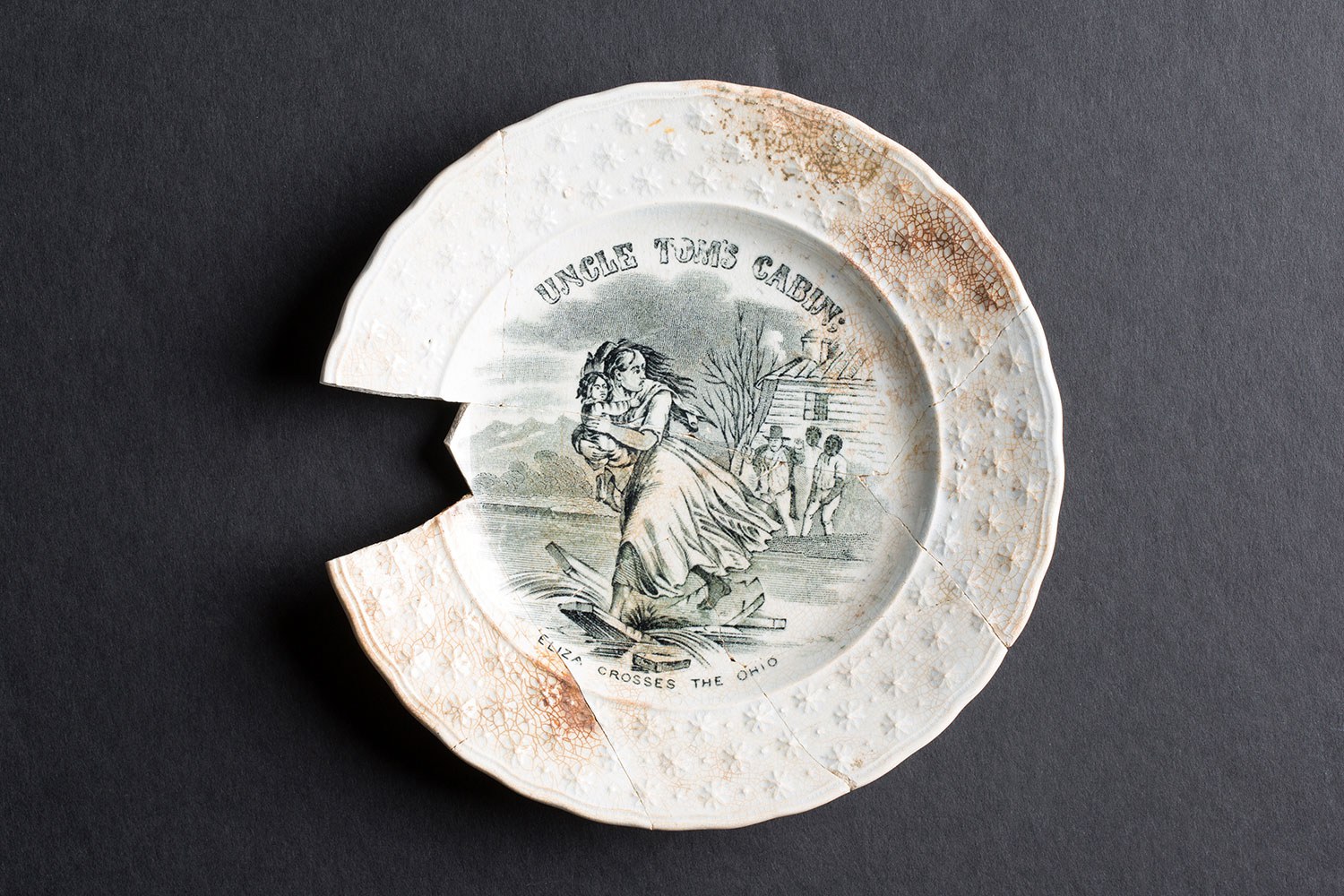
1852 – Uncle Tom’s Cabin, by Harriet Beecher Stowe, is first published in book form; it sells 300,000 copies in its first year of publication
1853 – On March 24, The Provincial Freeman is founded by Mary Ann and Isaac Shadd; The Provincial Freeman was an abolitionist newspaper; Mary Ann Shadd Cary was the first African-American woman to be published in North America
1857 – The ruling in Missouri in the Dred Scott case states that the enslaved in the United States are not humans, but property
1858 – On May 8, John Brown holds a convention in Chatham, Ontario where he plans to overthrow the American government and the entire slave system by means of guerilla warfare; on December 2, 1859, John Brown is executed in Charles Town, West Virginia after his attempted rebellion fails
1863 – Emancipation Proclamation is ordered by American President Abraham Lincoln declaring all slaves to be free
1865 – Thirteenth Amendment officially abolishes slavery in the United States
1922 – Lincoln Alexander is born; he later becomes the first Black Member of Parliament, the 24th Lieutenant-Governor of Ontario and Ontario’s first Black lieutenant-governor; Alexander is also a member of the Order of Ontario and a Companion of the Order of Canada
2007 – Bicentennial commemoration of the abolition of the trans-Atlantic slave trade




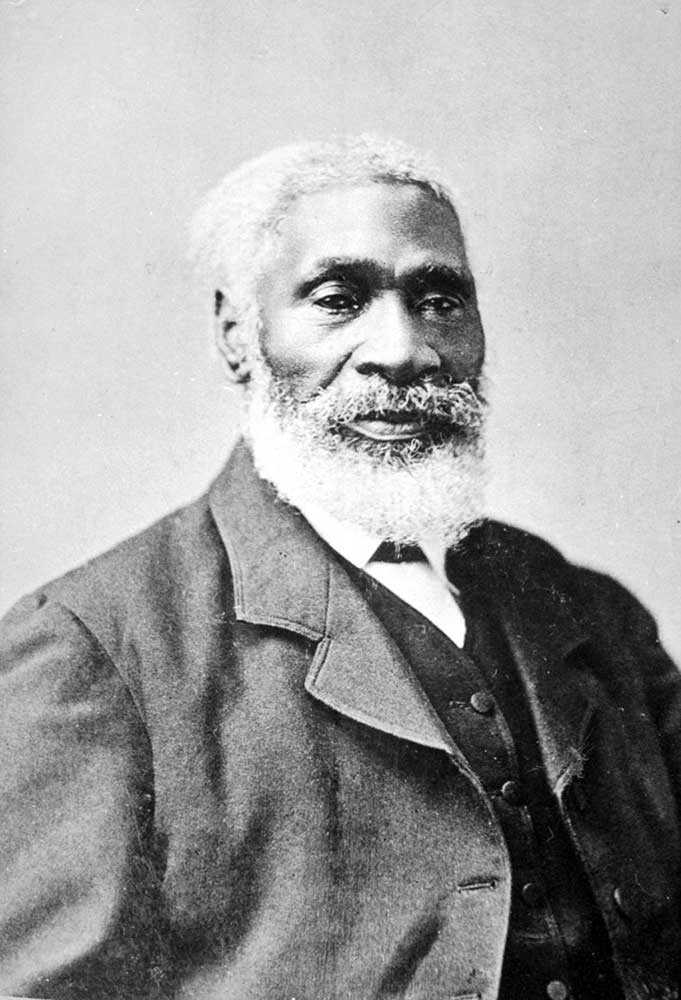


![F 2076-16-3-2/Unidentified woman and her son, [ca. 1900], Alvin D. McCurdy fonds, Archives of Ontario, I0027790.](https://www.heritage-matters.ca/uploads/Articles/27790_boy_and_woman_520-web.jpg)




























